WCSS Researchers Reveal the Functionalizing Framework Nucleic-Acid-Based Nanostructures for Biomedical Application
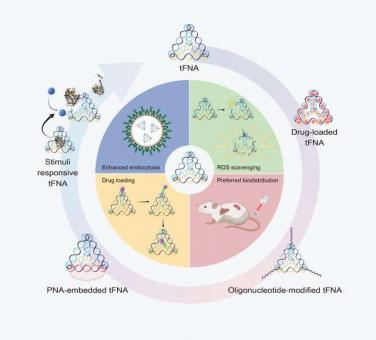
Fabrication strategies and potential applications of tFNA-based nanostructures in biomedicine.
Researchers from West China School of Stomatology (WCSS), Sichuan University, revealed the detailed strategies for functionalizing tetrahedral framework nucleic acids (tFNAs), emphasizing their potential biomedical applications, including tissue engineering, anti-cancer and anti-bacterial therapy. The research was published in the journal Advanced Materials.
The three fabrication methods of tFNA are first introduced, in which the one-pot annealing method optimized the cost, yield and speed of assembly. In addition to the promising biocompatibility and structural stability, four key merits of tFNA including the nature ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species, remarkable enhancement in cellular endocytosis and tissue permeability based on its appropriate size and geometry, promoting cell-material interaction to direct or probe cell behavior, especially to treat inflammatory and degenerative diseases, are also discussed. Then, the authors emphasized strategies for functionalizing tFNA. Based on the principle of Watson–Crick base pairing, peptide nucleic acid, siRNA, miRNA and DNA aptamer could be located to the vertex of tFNA via sticky-end binding and direct ligation. Through incubation at room temperature and other methods, a variety of Chinese traditional medicine monomers such as wogonin, resveratrol (RSV) and curcumin, along with antimicrobial peptide GL13K could also be loaded into tFNA structure. In addition, strategies in constructing dynamic tFNAs via attachment of stimuli-responsive DNA apparatuses is also involved. The tFNA-based functional nanostructures have been successfully applied in targeted therapies, tissue regeneration, antitumor strategies, and antibacterial treatment.
The work was supported by Sichuan University. Prof. Yunfeng Lin, the leader of the research team, is the corresponding author. Associate researcher Tao Zhang and postdoctoral fellow Taoran Tian are the co-first authors of the paper.
For more details of this study, please click the link below.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202107820
https://www.webofscience.com/wos/alldb/full-record/WOS:000758096000001




